The Historic Panagyrushte Treasure: A View Into Thrace’s Golden Past
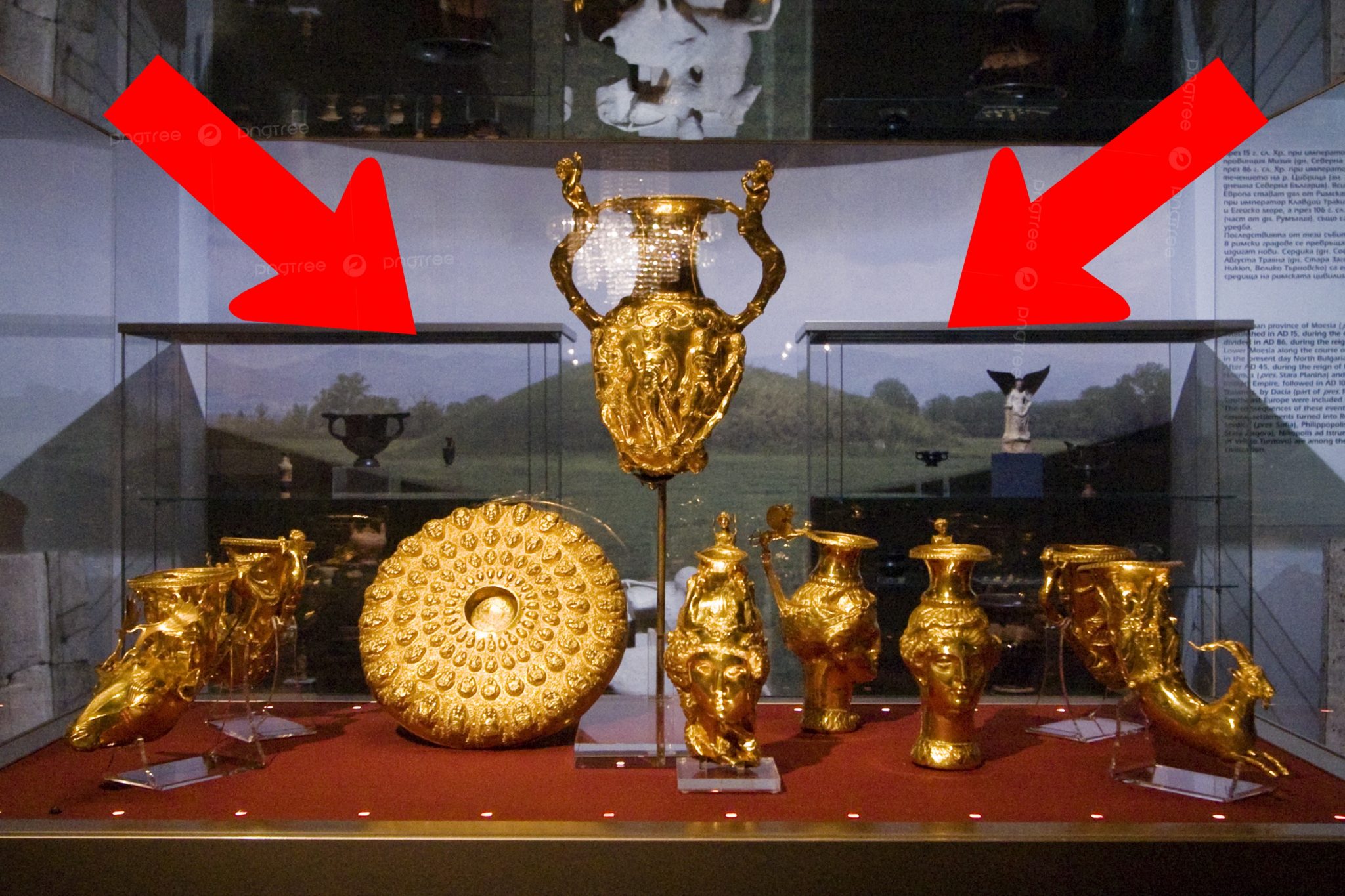

Dating back over 2,400 years ago, the Panagyurishte Treasure stands as a testament to the opulence and craftsmanship of ancient civilizations. Discovered in the Bulgarian town of Panagyurishte in 1949, this extraordinary collection comprises nine vessels crafted from 24-karat gold, weighing a total of 6.1 kilograms. Believed to have been used ceremonially by the Thracian King Seuthes III, this treasure has captivated the imagination of historians, archaeologists, and art enthusiasts alike, offering a glimpse into a bygone era of wealth and cultural sophistication.
The unearthing of the Panagyurishte Treasure marked a pivotal moment in the field of archaeology, unveiling a trove of artifacts that shed light on the artistic and technological achievements of ancient Thracian civilization. Each vessel within the collection is a masterpiece of goldsmithing, meticulously crafted with astonishing precision and adorned with intricate motifs and designs.
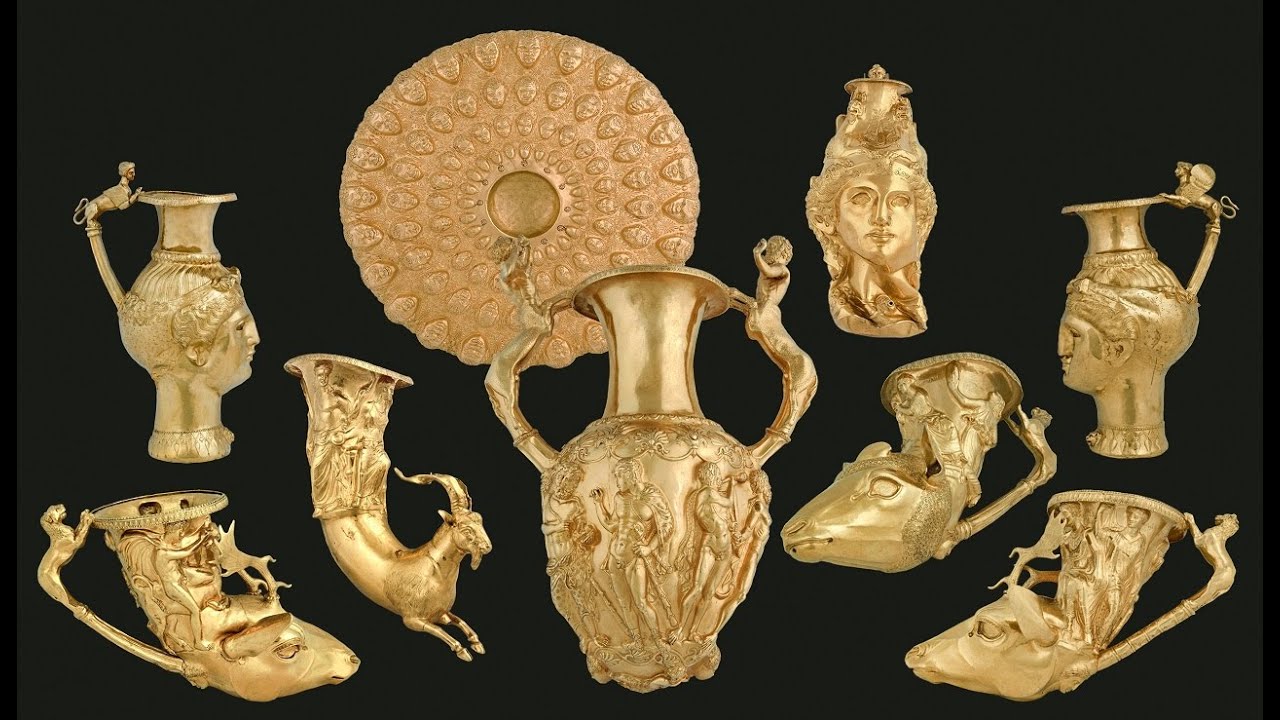
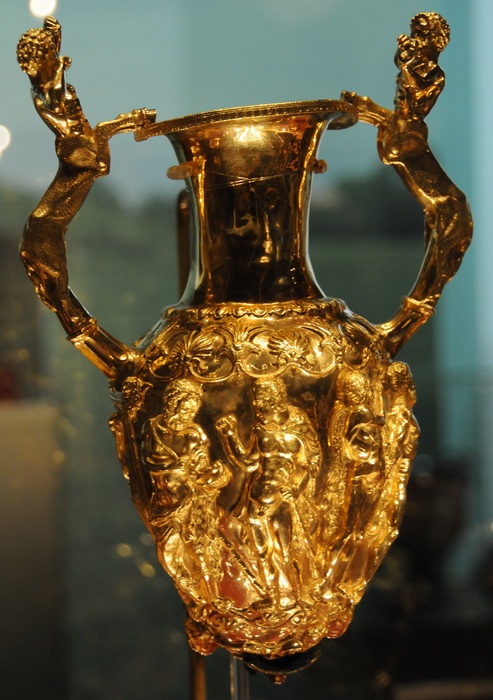
The centerpiece of the treasure is the famous Panagyurishte phiale, a shallow ceremonial bowl adorned with richly detailed relief scenes depicting mythological figures, animals, and floral motifs. Its exquisite craftsmanship and symbolic imagery suggest that it played a significant role in religious or royal ceremonies, serving as a vessel for libations or offerings.
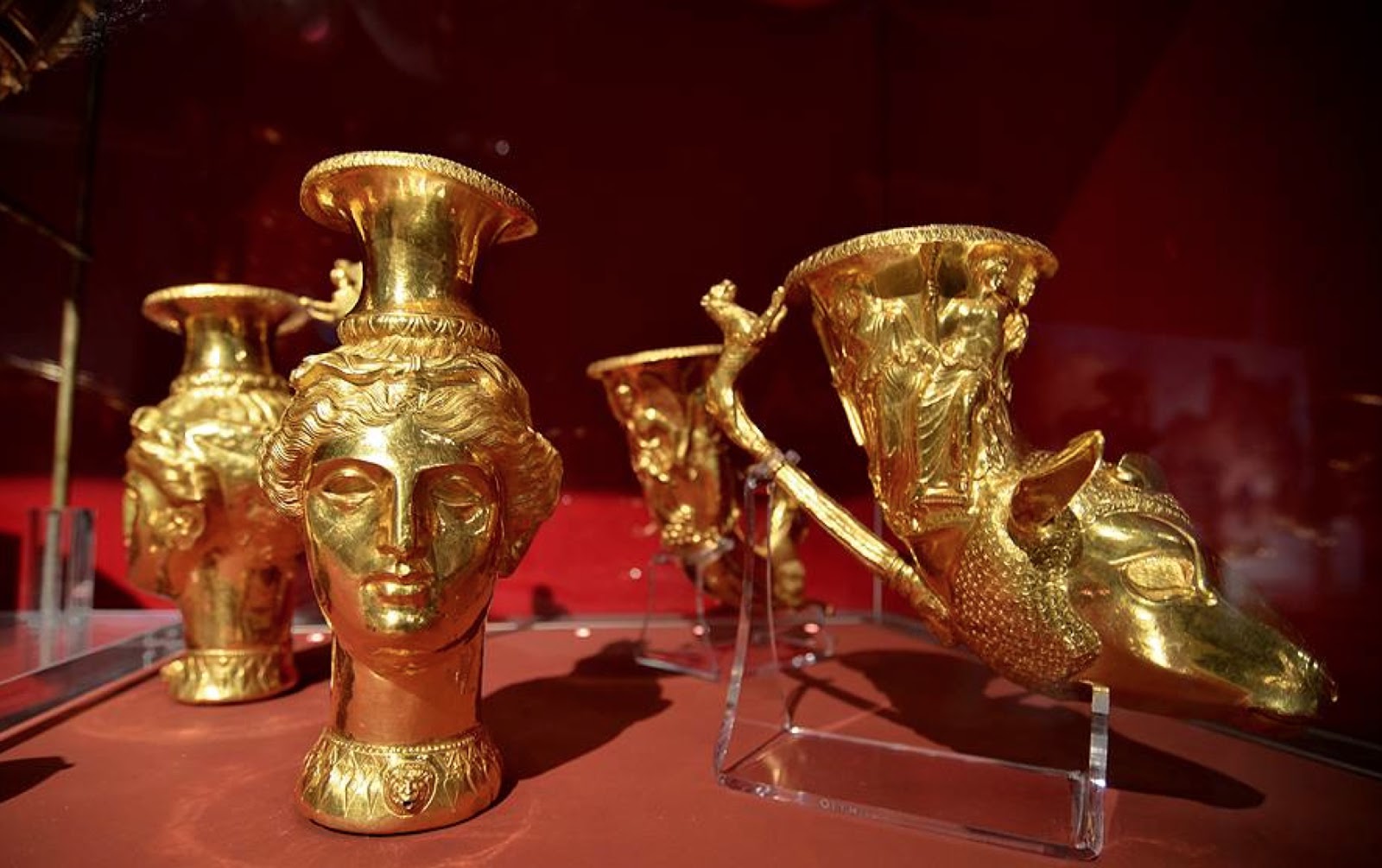
Accompanying the phiale are eight rhytons, or drinking horns, each uniquely crafted with elaborate handles and sculpted animal heads. These vessels, designed for ritualistic drinking, symbolize the social and ceremonial importance of feasting and communal gatherings in ancient Thracian culture. The sheer artistry and craftsmanship displayed in the construction of these rhytons attest to the Thracians’ mastery of metallurgy and their reverence for precious materials.

Beyond their aesthetic appeal, the Panagyurishte Treasure provides valuable insights into the socio-political dynamics of ancient Thrace. As one of the most significant archaeological finds in Bulgaria, it has sparked debates among scholars regarding its origins, purpose, and significance. Some suggest that it was created as a tribute to King Seuthes III, commemorating his reign and affirming his status as a divine ruler. Others propose that it served as a diplomatic gift or offering to solidify alliances and maintain regional power dynamics.
The discovery of the Panagyurishte Treasure continues to inspire ongoing research and exploration into the cultural heritage of ancient Thrace. Through interdisciplinary collaboration and advanced scientific techniques, archaeologists strive to unravel the mysteries surrounding its creation and significance. Chemical analysis and metallurgical studies offer insights into the composition and production techniques of the artifacts, while comparative studies with other archaeological finds provide context for understanding their cultural and historical significance.

Moreover, the Panagyurishte Treasure serves as a poignant reminder of the importance of preserving our cultural heritage for future generations. As a symbol of Bulgaria’s rich history and cultural legacy, it remains a source of national pride and identity, showcasing the artistic achievements of ancient civilizations and their enduring impact on contemporary society.
In conclusion, the Panagyurishte Treasure stands as a remarkable testament to the artistic ingenuity and cultural richness of ancient Thrace. From its stunning craftsmanship to its enigmatic symbolism, each artifact offers a window into a distant past, inviting us to unravel its secrets and discover the stories it holds. As we continue to study and appreciate this extraordinary collection, we reaffirm our commitment to preserving and celebrating the diverse tapestry of human history.