Roman Swords Dating Back 1,900 Years Discovered in a Dead Sea Cave
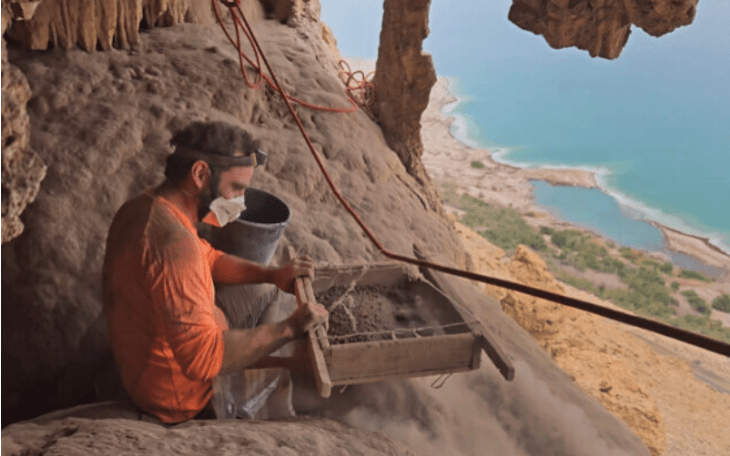

Archaeologists have discovered four 1,900-year-old Roman swords in a cave in the Judean Desert, which experts believe were captured by the Judean rebels during the Bar Kochba revolt and placed in a narrow crevice in the rock.
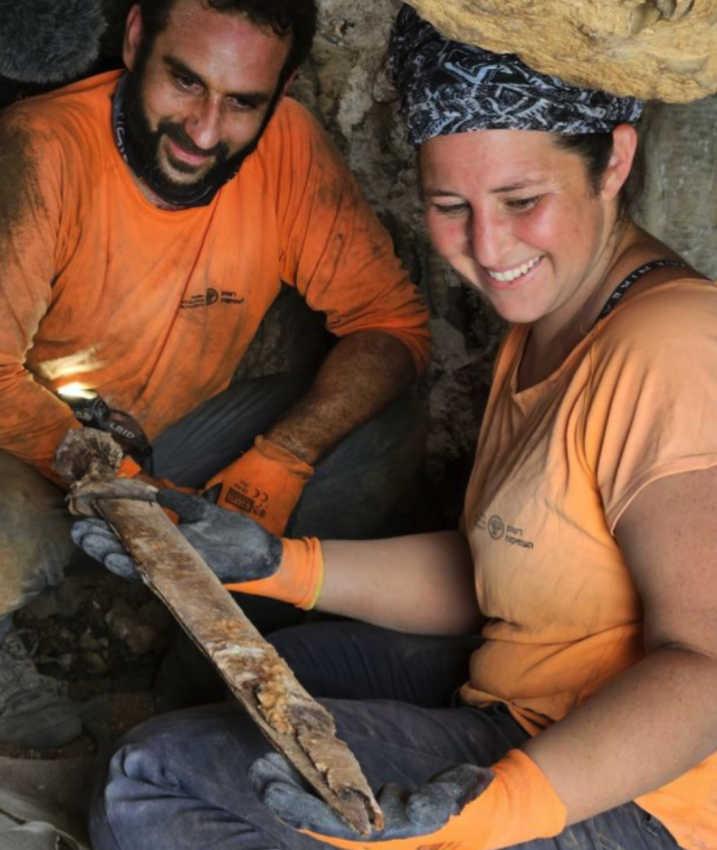

“We’re talking about an extremely rare find, the likes of which have never been found in Israel,” Dr. Eitan Klein, one of the directors of the Israel Antiquities Authority’s Judean Desert Survey, said in a video accompanying the announcement of the discovery. “Four swords amazingly preserved, including the fine condition of the metal, the handles, and the scabbards.”
The preliminary article on the swords is published in the volume “New Studies in the Archaeology of the Judean Desert: Collected Papers,” which explores new archaeological finds discovered in the Judean Desert Survey Project. A conference launching the book is taking place Wednesday in Jerusalem.

The four swords were discovered shoved into a small fissure in a cave near Ein Gedi National Park, near the Dead Sea. The cave is already well-known to archaeologists, as it contains a stalactite with a fragmentary ink inscription written in ancient Hebrew script characteristic of the First Temple period.
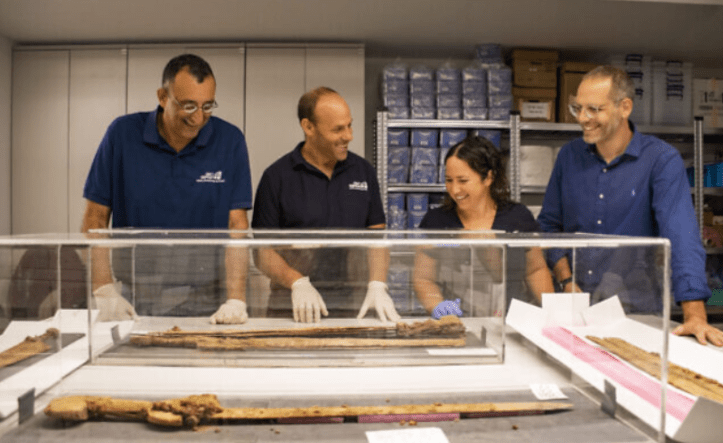

Recently, Dr. Asaf Gayer of Ariel University, geologist Boaz Langford of Hebrew University, and Israel Antiquities Authority photographer Shai Halevi returned to the cave to photograph the stalactite with multispectral photography, which can decipher additional parts of the inscription not visible to the nɑƙeɗ eye. While inside the cave, Gayer spotted an extremely well-preserved Roman pilum — a shafted weapon — in a deep, narrow crack in the rock. He also found pieces of carved wood in an adjacent niche that turned out to be parts of the swords’ scabbards.
Get The Times of Israel’s Daily Editionby email and never miss our top storiesNewsletter email addressBy signing up, you agree to the terms
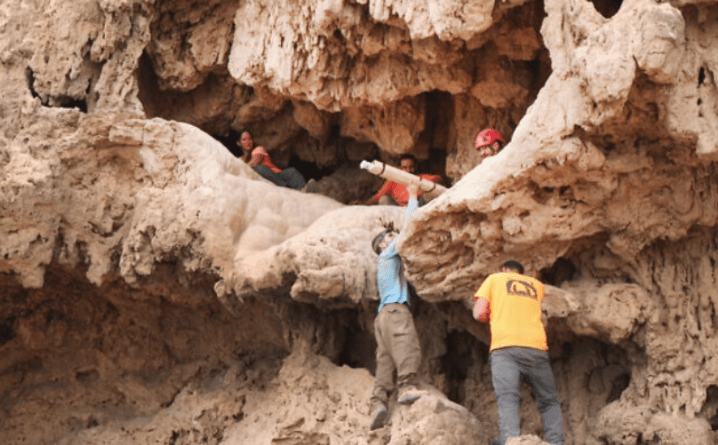

The researchers reported the find to the Israel Antiquities Authority and returned to the site with the Judean Desert Archaeological Survey Team, which is conducting a multi-year comprehensive survey of more than 800 caves in the Judean Desert to find and preserve archaeological remains before they are looted.
It was then that they discovered the four swords, three of which were found with the blades still inside their scabbards. Researchers also found ornate handles made of wood and metal with leather ᵴtriƥs nearby. The arid climate in the Judean Desert helps preserve fragile artifacts that might otherwise be lost to the ravages of time, including materials such as leather and wood, which are rarely found in wetter parts of the country.